17135번: 캐슬 디펜스
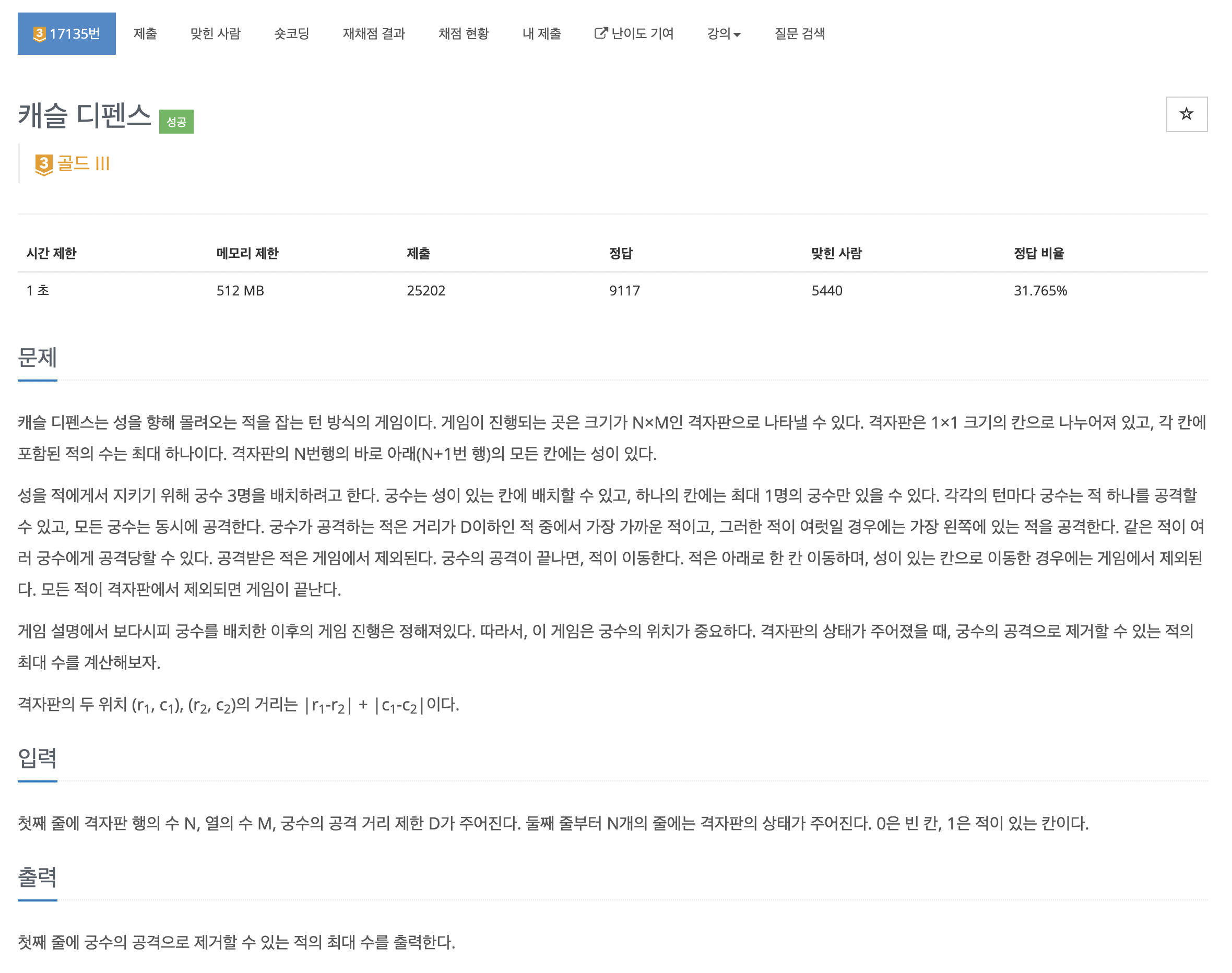
첫째 줄에 격자판 행의 수 N, 열의 수 M, 궁수의 공격 거리 제한 D가 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 격자판의 상태가 주어진다. 0은 빈 칸, 1은 적이 있는 칸이다.
www.acmicpc.net
문제를 읽고 적이 아래로 한칸 이동한다를 "궁수가 한칸씩 위로 이동한다" 라고 생각하였다.
(board 자체를 수정하지 않고, 궁수 배열을 따로 관리하며 row를 바꾸는것이 더 간단하다고 생각하였기 때문)
로직은
1. 궁수 3명의 index(column)를 정하여 archer 배열로 선언한다 (조합)
2. archer의 row를 N+1부터 1까지 (역순으로) 변경하며 가장 가까운 적을 제거한다.
2-1. archer의 좌표가 (r, c)라면 (r-1, c)부터 좌, 우, 상 방향으로 이동하며 distance를 1씩 증가시키며 bfs를 실행한다.
2-2. 가장 가까운 적의 좌표를 current enemy set에 저장한다.
2-3. 3명의 archer 모두 탐색한 뒤 current enemy set에 있는 좌표를 통해 board를 변경한다 (board[x][y] = 1)
2-4. current enemy set을 enemy set과 합친다.
2-4. r을 하나 감소시키고 (궁수를 한칸 전진 시키고) 2-1부터 다시 시작한다.
3. enemy set에 있는 좌표를 통해 board를 변경한다. (board[x][y] = 0, 죽은 적을 되살린다.)
4. enemy set의 길이를 return한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
import sys
from collections import deque
direction = ((0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, 0))
def bfs(r, c):
queue = deque([(1, r-1, c)])
visit = set()
visit.add((r-1, c))
min_distance = float('inf')
min_x, min_y = -1, -1
while queue:
d, x, y = queue.popleft()
if min_distance < d: break
if board[x][y] == 1:
if min_distance == float('inf'):
min_distance = d
min_x, min_y = x, y
else:
if min_y > y:
min_x, min_y = x, y
if d == D: continue
for dx, dy in direction:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if not (0 <= nx < N and 0 <= ny < M): continue
if (nx, ny) in visit: continue
queue.append((d+1, nx, ny))
visit.add((nx, ny))
return (min_x, min_y)
def attack_simulation(archer):
dead_enemy = set()
for archer_row in range(N, 0, -1):
cur_dead_enemy = set()
for archer_col in archer:
near_enemy = bfs(archer_row, archer_col)
if near_enemy == (-1, -1): continue
cur_dead_enemy.add(near_enemy)
for x, y in cur_dead_enemy:
board[x][y] = 0
dead_enemy |= cur_dead_enemy
cnt_dead_enemy = len(dead_enemy)
for x, y in dead_enemy:
board[x][y] = 1
return cnt_dead_enemy
def solve():
answer = 0
archer = []
for a in range(M):
archer.append(a)
for b in range(a+1, M):
archer.append(b)
for c in range(b+1, M):
archer.append(c)
answer = max(answer, attack_simulation(archer))
archer.pop()
archer.pop()
archer.pop()
return answer
N, M, D = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
board = [list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())) for _ in range(N)]
print(solve())
|
문제 자체는 어렵지 않았지만, bruteforce 방식으로 simulation하다보니 코드의 길이가 길어졌다.
조합을 직접 구현하기보다 combinations 패키지를 사용한다면 조금 더 깔끔하게 구현이 가능할 것 같다.
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 / 1520 / 내리막 길 / 파이썬, python, pypy (0) | 2022.09.22 |
|---|---|
| 백준 / 24040 / B 예쁜 케이크 / Good Bye, BOJ 2021! / 파이썬, python, pypy (0) | 2022.01.02 |
| 백준 / 1393 / 음하철도 구구팔 / 파이썬, python, pypy (0) | 2021.11.21 |
| 백준 / 15824 / 너 봄에는 캡사이신이 맛있단다 / 파이썬, python, pypy (0) | 2021.09.07 |
| 백준 / 11689 / GCD(n, k) = 1 / 파이썬, python, pypy (0) | 2021.09.03 |
